Tag Archive for: foresight
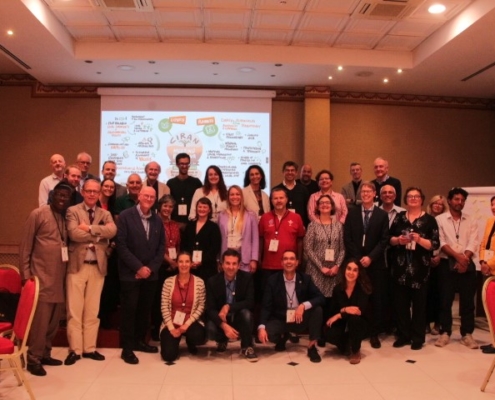

CIRAN 3rd Consortium Meeting (Bologna, Italy)
From September 30 to October 3 2024, the CIRAN project team gathered…
 La Palma Research Centre
La Palma Research CentreFutures Conference 2023 – Empowering Futures, 14-16 June 2023, Turku, Finland
The La Palma Research Centre team joined a community of futures…
Call for experts – ROBOMINERS Delphi Survey
The LPRC team would like to invite you to answer to the ROBOMINERS…

INTERMIN project Final Review Meeting
The INTERMIN project held its Final Review Meeting with the EC…

LPRC contributes to the MOBI-US Training event – Part 1
The MOBI-US project has reached one more important milestone…

ROBOMINERS e-Consortium meeting, 7th September 2020
The ROBOMINERS consortium, where LPRC participates and leads…

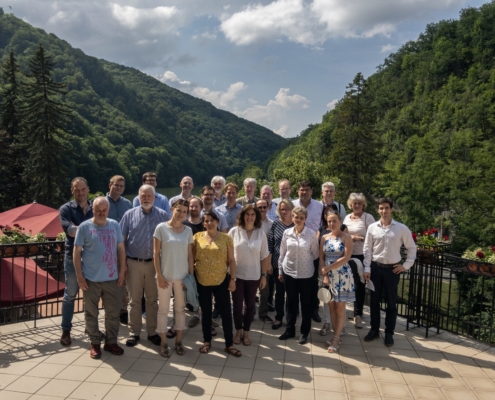
ROBOMINERS Consortium Meeting, Tallinn
It was in Tallinn, Estonia, that the ROBOMINERS project partners…
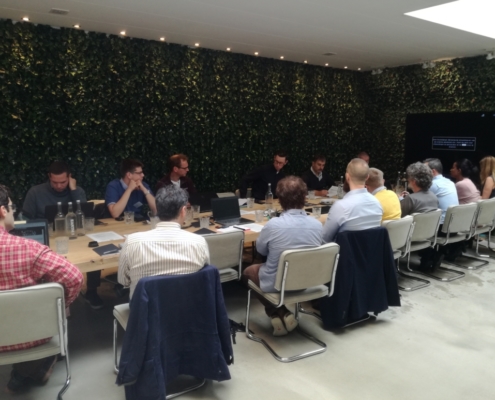

ROBOMINERS/UNEXMIN Joint Workshop, Amsterdam
Luís Lopes, responsible for Communication and dissemination…
 Tamas Miklovicz
Tamas MikloviczCHPM2030 project closure
CHPM2030 Final meeting
The CHPM2030 project partners met in…

Constructing Social Futures conference, Turku
Constructing Social Futures - Sustainability, Responsibility…
